
MRI of the abdomen in the axial plane (A), showing distention of the... Download Scientific
use: most widely used axial plane for MRI and increasingly for CT Schaltenbrand definition landmarks: from the center of the anterior commissure and the center of the posterior commissure brainstem vertical line landmarks: a line perpendicular to the posterior surface of the brainstem orbitomeatal line

MRI of the Brain Axial Plane. Stock Image Image of diagnosis, cerebrum 154453905
Axial MRI Atlas of the Brain. Free online atlas with a comprehensive series of T1, contrast-enhanced T1, T2, T2*, FLAIR, Diffusion -weighted axial images from a normal humain brain. Scroll through the images with detailed labeling using our interactive interface. Perfect for clinicians, radiologists and residents reading brain MRI studies.

Healthcare Extreme How To Read An MRI Lumbar Spine In 8 Easy Steps
According to the original meaning of the word, the angle of "axial" MR images is vertical to the bed of the equipment. However, with the development of oblique imaging in the late 1980s, "axial" has come to mean a range of angles. At the present time, brain axial images are oblique, and six different angles are used.

T1 axial plane MRI of the brain. Download Scientific Diagram
The landmarks on the midsagittal MR image to determine the angle of the reference lines are as follows: the supraorbito-meatal line (the center of the mammillary body and the fastigium of the fourth ventricle), the orbito-meatal (OM) line (the center of the mammillary body and the most posterior point of the cerebellar tentorium), the Talairach.

Figure 6 from A guide to identification and selection of axial planes in resonance
CT evaluation of diffuse infiltrative lung disease: dose considerations and optimal technique. J Thorac Imaging. 2009;24:252-259. HRCT Primer. Image Reconstruction Planes. Review the different image reconstruction planes, which include axial, coronal, and sagittal planes and are made possible using volumetric acquisition CT.

(a) Axial plane contrastenhanced MRI demonstrating lesion at time of... Download Scientific
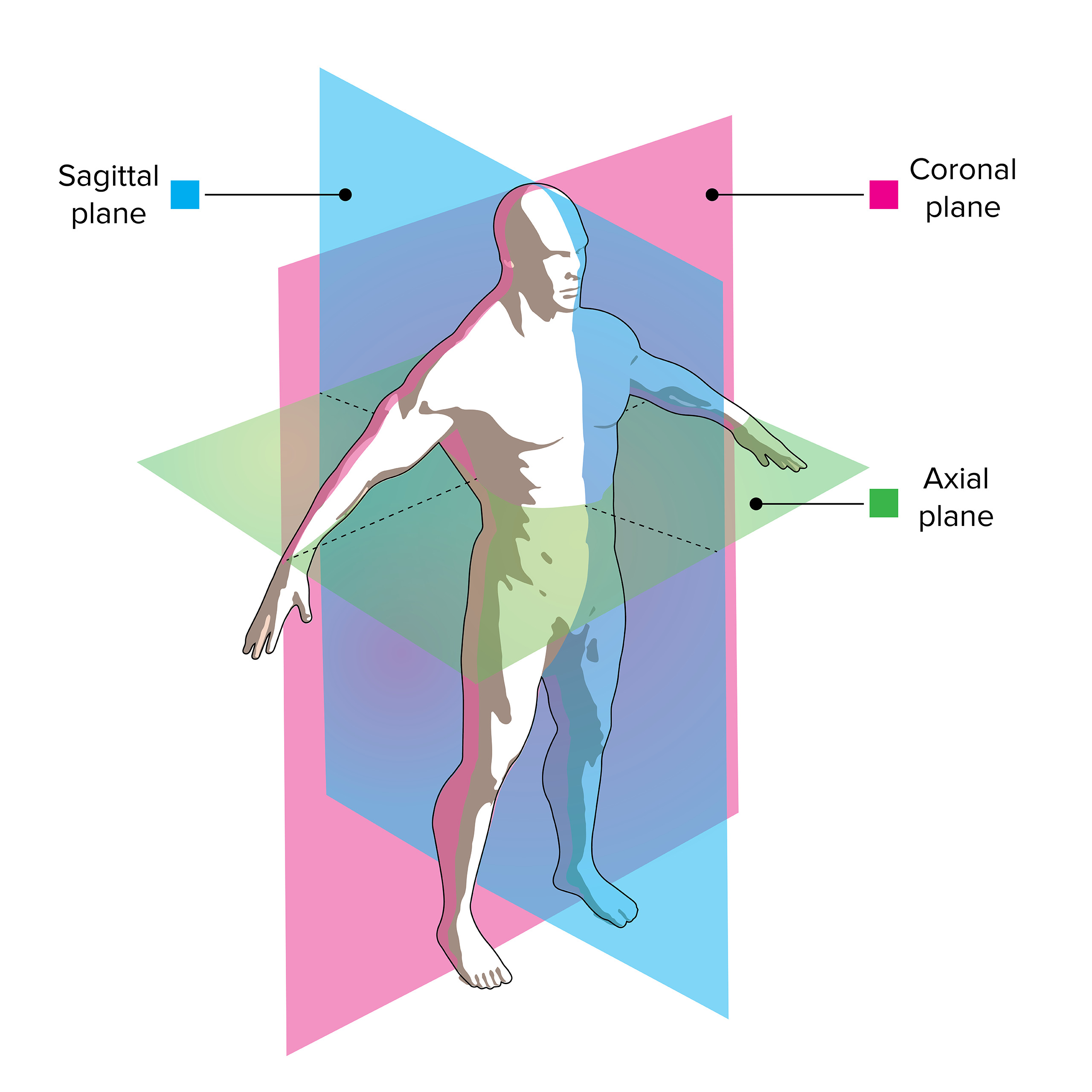
Anatomical planes are imaginary planes/2D surfaces used to divide the body to facilitate descriptions of location and movement. The anatomical position is used as a reference when describing locations of structures and movements. It is an upright position with arms by the side and palms facing forward. Feet are parallel with toes facing forward.
Imaging of the Spine and Spinal Cord Concise Medical Knowledge
Recommended Hip MRI Protocols, Parameters, and Planning. MRI hips localizer. A three-plane localizer must be taken at the beginning to localize and plan the sequences. Localizers are normally less than 25 seconds, T1-weighted low-resolution scans.. Plan the coronal slices on the axial plane; angle the positioning block parallel to the RT and.

Axial Plane of Human Brain Download Scientific Diagram
MRI Faculty William Dillon, MD Professor Executive Vice-Chair Medical Director for Ambulatory Imaging Share this video UCSF Radiologist Dr. Dillon describes how radiologists read images. The different planes that Radiologists use are axial (divides the body into top and bottom halves), coronal (perpendicular), and sagittal (midline of the body).

T2 weighted highresolution MRI in axial plane showing the typical... Download Scientific Diagram
MRI Basics. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Brain and Spine: Basics. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most commonly used tests in neurology and neurosurgery. MRI provides exquisite detail of brain, spinal cord and vascular anatomy, and has the advantage of being able to visualize anatomy in all three planes: axial.

Figure 10 The MRI images in three orthogonal planes (sagittal, coronal, and axial) in a 1.5
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the modality of choice for investigating painful hip conditions due to its multiplanar capability and high contrast resolution. This review focuses on the characteristic MRI features of common traumatic and pathologic conditions of the hip.

The 18 anatomical landmarks on a T1weighted MRI. (A) Axial plane at... Download Scientific
Look at each available plane (axial, coronal, sagittal) Check for abnormal MRI signals; Work through the anatomy of the areas you are looking at to make sure nothing is missed/abnormal; Comparing both sides of an image (if possible) can reveal clear areas of abnormal signalling; Shape, size, location, and intensity of the signal

Understanding Brain MRI Planes and Cuts Resonance Imaging 101 YouTube
MRI. The hippocampus is best imaged in the coronal plane, angled perpendicular to the long axis of the hippocampal body. The three parts of the hippocampus (head, body and tail) can be identified based on morphology and by using local landmarks 3. amygdala-hippocampal head junction. landmarks. anterior lobe of the pituitary to basilar artery

Axial plane MRI obtained by CISS sequence. A right medial superior... Download Scientific Diagram
The landmarks on the midsagittal MR image to determine the angle of the reference lines are as follows: the supraorbito-meatal line (the center of the mammillary body and the fastigium of the fourth ventricle), the orbito-meatal (OM) line (the center of the mammillary body and the most posterior point of the cerebellar tentorium), the Talairach.

Atlas JHP MRI Brain Atlas
In the X-Y-Z coordinate system, axial is an X-Y plane, parallel to the ground, the head from the feet. A coronal is an X-Z plane, the front from the back. A sagittal is a Y-Z plane, which.

Anatomical planes of a human body as captured during MRI Download Scientific Diagram
The pars marginalis, II: a "bracket" sign for the central sulcus in axial plane CT and MRI.. Int J Neuroradiol 1996; 2: 20-24. ↵. Naidich TP, Brightbill TC. Systems for localizing fronto-parietal gyri and sulci on axial CT and MRI. Int J Neuroradiol 1996; 2: 313-338. Valente M, Naidich TP, Abrams KJ, Blum JT.

Brain MRI. Axialplane Flair T2wheigted sequences reveal multiple... Download Scientific Diagram
T2 stir coronal 3mm. Plan the coronal slices on the axial plane and angle the planning block parallel to the right (RT) and left (LT) optic nerve. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane (perpendicular to the optic nerve). Ensure that the slices are sufficient to cover the.